Choosing the Right PV System
Guidelines to Quality
A guide to a long-term investment
The decision to purchase a photovoltaic (PV) system is a long-term investment and for this reason must be selected with great care. The system is expected to operate at extreme weather conditions for over 20 years and must prove to deliver the electricity output (financial output) and performance but also to be safe and durable.
In principle, the selection of which PV module and inverter, and from which manufacturer/installer the system will be purchased, is a process that requires careful consideration.

Technical specifications
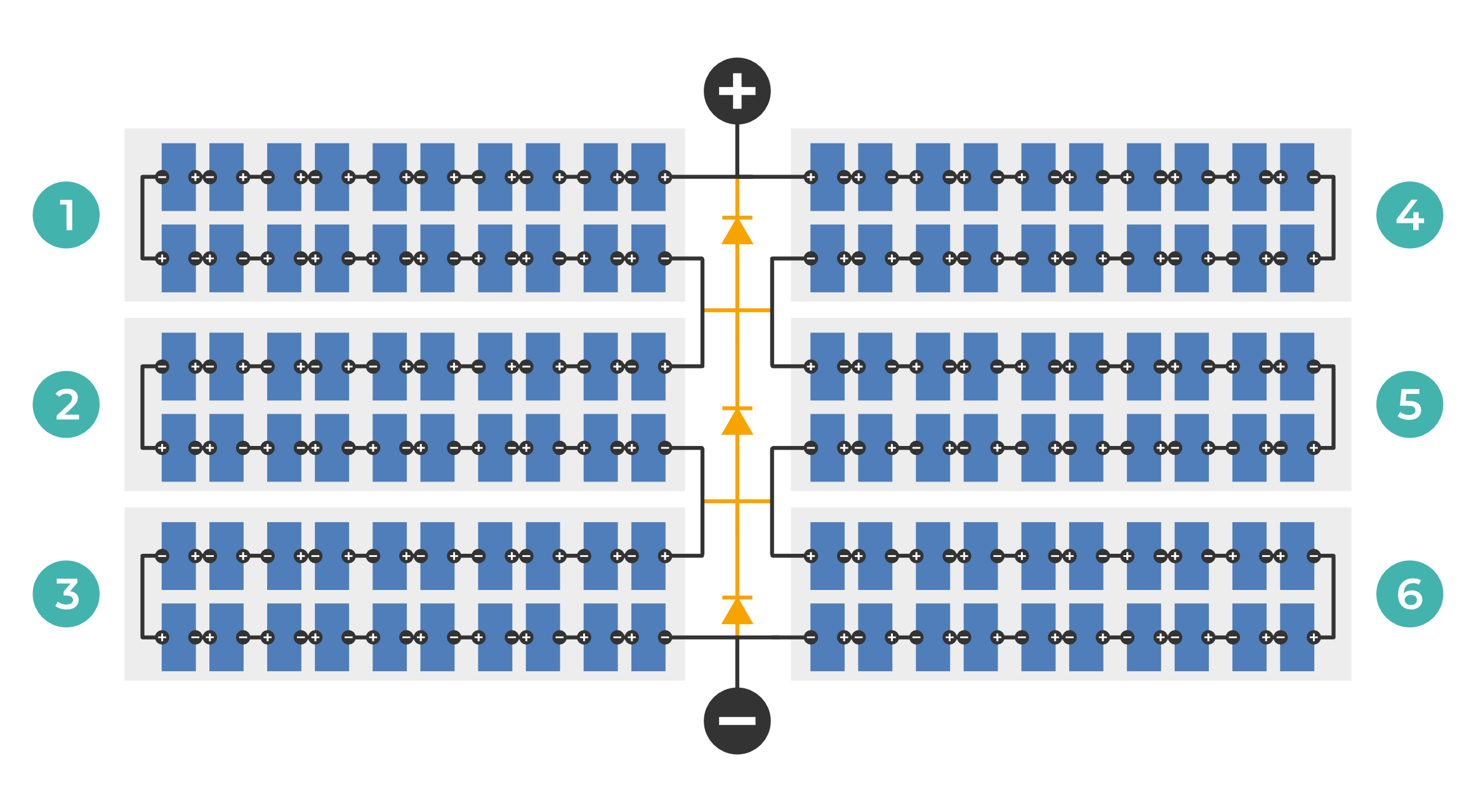
PV Modules
Quality criteria for PV modules
N-Type VS. P-Type Solar Panels
PV cells consist primarily of a crystalline silicon wafer supplemented with additional materials to facilitate electricity generation.
In a P-type cell, a silicon base is doped with boron atoms to establish an overall positive charge, hence denoted as ‘P’ type. The upper silicon layer of the wafer is doped with phosphorus (N-type) to establish a p-n junction for electron flow. P-type cells are the predominant variant employed in solar panel manufacturing.
Conversely, N-type cells exhibit an inverse configuration compared to P-type cells. They feature a silicon base doped with phosphorus, resulting in an overall negative charge. The top layer of N-type silicon cells is doped with boron (P-type) to facilitate the formation of the p-n junction.
N-type modules
P-type modules
Inverter
Quality criteria for inverter
Mounting structure
Quality criteria for mounting structure
Quality
standards
Certifications for PV modules
General certifications
Additional test standards
Certifications for inverters
General certifications
Companies
Module and inverter manufacturers must hold a quality Assurance certificate ISO: 9001:2015 or equivalent, regarding the manufacture and sales of solar modules and inverters, respectively.
Top quality manufacturers ensure that:
- Quality checks are applied on the production line.
- Selection is made of quality products.
- Investments are made to upgrade production lines and invest in research and innovation.
- Consider high quality standards in packaging products.
- Attention is given to customer experience and satisfaction.
Another important parameter is to select a PV module that is Tier 1 according to Bloomberg New Energy Finance (BNEF) classification since this indicates that the manufacturer has a strong track record of producing reliable and high-quality PV modules. These manufacturers typically invest heavily in research and development, quality control processes, and adhere to industry standards, resulting in products with lower failure rates and longer lifespans.
This can help ensure the success and longevity of solar projects by minimizing risks associated with quality, performance, and bankability.
Installation companies need to exhibit experience in the field, have technical training in relevant technical courses, ease of communication and reach, and low time for error resolution.
Warranty
Warranty for PV modules
Product warranty
≥ 10 years
Performance guarantee
First year: > 98%
After first year: < 0.5% annual degradation
Warranty for inverters
Product warranty
≥ 10 years
Failure
examples
Useful Links
This section provides a set of useful links to pertinent resources.